Prostatitis is the most common urological pathology in men of reproductive age. According to polls, at least once in his life, he has experienced third symptoms that can be interpreted as inflammation of the prostate gland. Despite being so high pathology, prostatitis is still poorly examined.To date, there is no consensus that it becomes a starting point in inflammation, as only 10% of cases can distinguish between patients' geniturinary tract from patients.
The lack of clear diagnostic criteria and the lack of characteristic symptoms of the disease complicate the accounting of patients. The symptoms of prostatitis are not so specific that each doctor interprets them largely with subjectivity and attributed to a completely different pathology. Accordingly, the approach to treatment also changes, and often patients go from one hospital cabinet to another, for years without positive dynamics. Prostatitis deprives one of confidence in sexual strength, hung his thoughts on one of the problems, and not as physical as psycho -emotional suffering.
What is the prostate and why is it necessary?
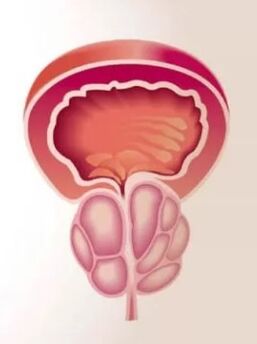
The prostate (prostate) is a small gland organ is a man located under the urethra under the urethra. It is tightly impaired to the urethra and forms one of its sphinctes - forms a muscle plant designed to keep urine. In the form and size of the prostate, it resembles a chestnut nut, which is often compared to anatomies. The part of the urethra, which passes inside the gland, is called prostatic. The rear convex part of the prostate is in contact with the rectum so it can be easily felt by rectal test. The anterior surface of the gland is close to the pubic joint and is linked to the moving connective tissue league, and the venous plexus lies between them.
The prostate gland consists of leberek, all of which are made by alveoli - small bags lined with secretion harness. The alveolite is connected by the output channels in the form of pipes that merge with each other, enlarge and eventually fall into a simple part of the urethra. Inside the secretory bags, the prostate juice is synthesized and accumulated, which includes the nutrients of the spermatosoids. This allows male short cells to maintain activity in the female body for 5 days, which significantly increases the chances of fertilization.
The enlightenment of the gland occurs during ejaculation. The prostate juice mixes with the secret of the testicles and accounts for 10-30% of the final amount of sperm. So,The prostate performs 2 main functions in a person's body:
- Involved in the urination process - keeps urine when muscle fibers are reduced and freely transferred when they relax;
- It ensures the viability of sperm, distinguishing the nutrient prostate juice.
What does the disease develop?
Prostatitis inflammatory changes in the prostate gland and it should be understood that they are not only under the influence of bacterial microflora.The causes of inflammation can be any factor that can lead to damage to the glandular tissue and the destruction of its cells.
As with all other fabrics, the inflammatory process of the prostate goes through certain stages:
- Change - Damage to prostate cells. The remains of cytoplasma squirrels, the fragments of the nucleus, and the membranes from the destroyed cells are transferred to the intercellular space - each for the immune system. Immunity cells are actively striving for lesion, penetrating from blood vessels and connective tissue. Biologically active substances are thrown at the site of the injury, under the influence of blood vessels and "reinforcing" cells.
- Expression - The liberation of the liquid part of the blood from the vessels.As a result of immune cells, the walls of the dilated blood vessels become permeable to the plasma and rushes into the lesion of damage. If it is on the surface of the hollow organ or the gland wire, the liquid part of the blood is released into the lumen, if the inflammation is tissue, swelling develops. Such a measure is required to restrict the focus of the damage and to prevent further spread of the pathogen.
- Proliferation is the replacement of similar or connective tissue for damaged cells.The proliferation mechanism is launched a little later than the events described above, and its path depends directly on the depth of the damage. The small focus of the destruction of the prostate tissue is replaced by the same functional cells and the organ completely restores its work. Deep disorders are allowed by scarring - replacing dead tissue with connective tissue elements. Chronic prostatitis can eventually lead to the entire atrophy of the prostate gland and to change the secretory tissue to Cicatrici.
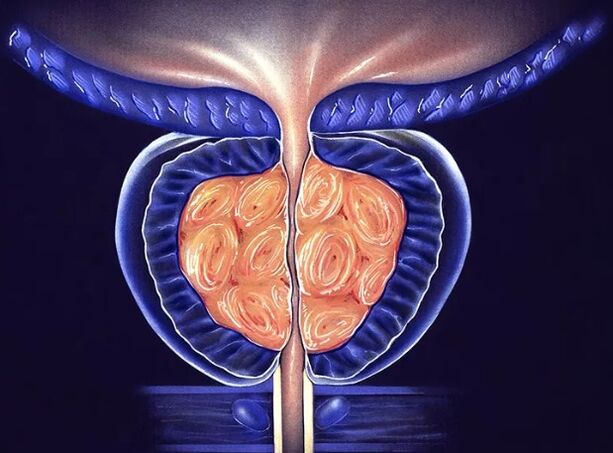
For the recommended reason, prostatitis is divided:
- Acute bacterium- Pathogenic microflora cause serious damage to the prostate tissues with a pronounced inflammatory reaction. Most often it develops with infection of gonococcus and other pathogens.
- Chronic bacterium-Treatment of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic bacteria causes slow inflammation, which remains for more than 2 months. As a general rule, the pathogens are Streptococci, Staphylococci, E. coli, Klebsiella, Mycoplasma, ureaplasma, chlamydia, herpesvirus and yeast -like marked fungus.
- Chronic abacter- In the presence of an inflammatory process, the causal microflora cannot be recognized in the prostate. A similar form of the disease develops when urine is poured into the prostate gland wires, stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis, violation of emptying (rare or too frequent ejaculation). In the latter case, the disease is called stagnating prostatitis.
How does the disease manifest?
The easiest to diagnose acute prostatitis,which continues with signs of intoxication and pronounced inflammation. In one person, the temperature suddenly rises to 38-39 ° C, pronounced pain in the perineum, in the rectum. They can give the groin, the testicles, to the penis, and are so unbearable that one's daily activities are sharply disturbed. In some cases, the body temperature measured in the axillary cavity does not exceed the normal indicators, but the rectum will always be 1-2 degrees per normal. Signs of prostatitis also become a violation of urination: severe urination, and then it is impossible to limit the acute delay of urine due to severe edema. Occasionally, the stool becomes painful as the size of the prostate has expanded into the lumen of the rectum.
Chronic prostatitisIt is so diverse in its shows that it can be easily confused with another pathology. In the most typical cases, symptoms of prostatitis are presented:
- Pain in the toe, pelvis.It is difficult for the patient to determine a specific place where he is localized, often pain in the lumbar, scrotum, penis head and stab. Its severity may differ: it is barely distinguished and intense stupid or pulling. Often pain is caused by urination or ejaculation, and occurs at the end of the process or at the beginning of the process.
- A violation of urination- The patient often urges the bladder to be emptied and has to get up several times at night to urinate. However, the pressure of the jet engine is normal and the urinary retention is rarely developed.
- Sexual disorders- In the background of the constant inconvenience at the foot of the man, the erection deteriorates and self -confidence disappears. The infringements get worse when the pain is related to the moment of ejaculation: the patient cannot completely relax because it expects discomfort.
As a general rule, in the case of chronic prostatitis, the general well of humans does not disturb, and body temperature remains normal throughout the disease.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis is determined by a doctor urologist or andrologistExamination of the patient, collecting anamnesis and studying symptoms. The doctor should find the patient's contraception method, the presence of STIs in a sexual partner, the possibility of anal relationships without a condom. These data facilitate diagnosis and control the doctor's thoughts in the right direction. The prescription of the symptoms of the disease or the discomfort in the perineum allows us to judge prostatitis and its severity. The urologist necessarily examines the patient's genitals and performs rectal examination of the prostate gland. To do this, he inserts one of his fingers into the patient's back passage and the protruding prostate is located on the front wall of the rectum. Pain and size indicate the intensity of the inflammatory process.
In addition, the doctor performs a number of instrumental, microscopic, bacteriological and immunological examination to clarify the cause of the disease. The most common diagnostic method is 4 or 3 bottles of urine pattern. The first method in practice is more time -consuming and difficult to practice, as the patient repeatedly requires consciously interrupting urination. The second modification is simpler: the patient is constantly urinated in three different containers in equal doses. The first part is about the condition of the urethra, the second about information about the pathology of the bladder and the kidneys, and the third information on the condition of the prostate gland. All the collected substances are tested under a microscope. In the case of prostatitis, the third part of the urine contains leukocytes and sometimes bacteria.
Access to study the prostate and massage when collecting secrets
The secret of the prostate gland is also taken for a microscopic examination.To do this, the doctor will make a prostate massage on the rectum wall for a while to empty it into the urethra. SMOPs are made from laboratory collected material, studied with painted and high growth. A sign of inflammation is leukocytes, bacterial -etiology of the disease - bacteria in smear. To determine the type of pathogen, the prostate secret is sown into nutrients. When it contains pathogenic microorganisms, they form microbial colonies after 3-5 days, which can be examined by bacteriological method, allowing for the sensitivity of the microflora to antibiotics.
Among the instrumental diagnostic methods : :
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- Prostate confidence with dopplerography - an ultrasonic sensor is inserted into the rectum for best display of the prostate gland, and its blood flow is also evaluated;
- Ugly rise is needed with a stubborn recurring prostatitis. An X -TRére contract is introduced into the urethra and then performs many consecutive images.

Treatment of chronic prostatitis should be tuned in a long struggle as it is not always possible to cure within a few weeks or even months. We recommend that you combine various methods and tools for therapy, and it is useful to improve household medication. Stagnant prostatitis requires regular sex and interrupted sexual acts are unacceptable. The patient's psycho -emotional background is important: depression, depression, personal life problems and sexual spheres can deny every effort of doctors.
How to prevent it?
Prevention of prostatitis involves:
- The use of contraceptive inhibition methods (condoms), especially for anal sex;
- Timely treatment of STI -K;
- Regular sex life, relationships for complete ejaculation;
- Preventing my leg injuries when classes, traumatic sports should be used with all possible protection methods;
- Adherence to personal hygiene;
- Ensure sufficient physical activity.
Despite the fact that prostatitis today is not related to the risk of developing adenoma or prostate cancer, the disease causes a lot of suffering to the owner. A man who is exhausted by chronic pain, feeling sexual weakness, is tired of prolonged treatment, becomes noticeably from the outside, and at first glance, such patients determine such patients. To avoid such a fate, you need to take care of your health, carefully protected with all new partners and treat sexually transmitted diseases in time. Prostatitis is not always completely treated, but an experienced urologist can significantly improve the patient's condition and the quality of his life.